CBD
What is CBD and How Does It Work in the Body?
Cannabidiol, more commonly known as CBD, has taken the health and wellness world by storm. From oils and tinctures to gummies and skincare products, CBD is now widely available and praised for its potential therapeutic effects. But what exactly is CBD, and how does it interact with the human body to provide these benefits?How to Read CBD Product Labels and Dosage Guides
CBD (cannabidiol) has become a popular natural remedy for various conditions, from anxiety and stress to chronic pain and sleep disorders. But with the growing number of products on the market—oils, gummies, capsules, topicals—choosing the right one can be overwhelming, especially if you don’t know how to read the label properly.
Understanding a CBD product label and dosage guide is essential for ensuring you’re buying a high-quality product, getting the correct dosage, and consuming it safely. In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about interpreting CBD labels and using dosage guides effectively.
Why CBD Labels Matter
CBD is still largely unregulated in many parts of the world, meaning not all products meet the same safety or quality standards. A product label is often the only source of information that tells you:
What’s in the product
How much CBD it contains
Whether it contains THC
How to take it and how much
If it’s been tested for safety and quality
By learning how to read CBD labels, you can make informed choices and avoid potentially misleading or low-quality products.
Key Elements of a CBD Product Label
Here are the main things to look for when reading a CBD label:
1. CBD Type: Full-Spectrum, Broad-Spectrum, or Isolate
Full-spectrum CBD: Contains all cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, including THC (usually less than 0.3%). Offers the “entourage effect.”
Broad-spectrum CBD: Contains all cannabinoids except THC.
CBD isolate: Pure CBD with no other cannabinoids or plant compounds.
Why it matters: This affects how the product interacts with your body and whether or not it will show up on a drug test.
2. Total CBD Content
Labels should list the total amount of CBD in the entire product, typically in milligrams (mg). For example:
A 30ml bottle may say “1000mg CBD”
A jar of gummies may say “300mg CBD” (for the entire container)
Pro tip: Check if the label also lists CBD per serving to understand dosage more clearly.
3. Serving Size and CBD Per Dose
Products should indicate how much CBD is in a single serving (e.g., 1 dropper, 1 gummy, 1 capsule). This helps you know how much to take.
Example:
“One dropper contains 33mg of CBD”
“Each gummy contains 10mg of CBD”
If a label doesn’t specify this, divide the total CBD by the number of servings.
4. Ingredients List
Always check the list of ingredients. Look for:
Carrier oils (like MCT oil, hemp seed oil, or olive oil)
Flavorings or additives
Other cannabinoids or herbal ingredients
Avoid products with artificial additives, unnecessary fillers, or ingredients you may be allergic to.
5. THC Content
Legal CBD products must contain less than 0.3% THC in the U.S. (or 0.2% in some other countries). Always check if the THC content is listed on the label.
If you want to avoid THC entirely, choose broad-spectrum or isolate products and verify this via lab reports.
6. Third-Party Lab Testing (COA)
Reputable CBD brands include a Certificate of Analysis (COA) from a third-party lab. This document verifies:
The CBD and THC content
Presence of other cannabinoids
Absence of harmful substances (pesticides, heavy metals, solvents)
You’ll often find a QR code on the label to scan for test results.
7. Expiration Date and Batch Number
High-quality CBD products should have:
An expiration date: CBD degrades over time.
A batch or lot number: Important for tracking quality control.
Avoid buying CBD without this information.
Understanding CBD Dosage Guides
CBD dosage isn’t one-size-fits-all. It depends on factors like body weight, individual tolerance, and desired effects. Here’s how to navigate a dosage guide.
1. Start Low and Go Slow
Most guides recommend starting with 5–10 mg of CBD per dose, especially if you’re new to it. Monitor how your body reacts, then gradually increase the dose until you find relief.
2. Consider Your Weight and Condition
A general guide is:
Body Weight Mild Effects Moderate Strong
100 lbs 10–15 mg 16–25 mg 26–40 mg
150 lbs 15–25 mg 26–40 mg 41–60 mg
200 lbs 20–30 mg 31–50 mg 51–75 mg
Note: Always consult a healthcare provider if you’re using CBD for medical reasons.
3. Product Type Affects Dosage
Different product forms vary in bioavailability—how much CBD actually enters your bloodstream:
Tinctures/Oils (under the tongue): 20–30% absorption
Gummies and Edibles: 10–15% (slower onset)
Vapes: Up to 50% (fastest absorption)
Topicals: Absorbed locally, not into bloodstream
Adjust your dosage based on how you’re taking it.
4. Frequency of Use
Some people take CBD once a day, while others take it multiple times depending on their needs. Follow the product’s suggested use and adjust as needed based on how you feel.
Red Flags to Watch Out For
Avoid CBD products that:
Don’t list the amount of CBD
Lack a COA or third-party testing
Contain vague or misleading claims (e.g., “cures everything”)
Are sold at prices too good to be true
Don’t specify the CBD type (full-spectrum, etc.)
Final Thoughts
Learning how to read CBD product labels and dosage guides is essential for safe and effective use. A well-labeled product will tell you exactly what you’re putting in your body and how to use it. Don’t settle for vague packaging—your health and safety are too important.
Always buy from reputable brands, start with a low dose, and consult your doctor if you’re taking medications or have health concerns. With the right knowledge, you can confidently choose a CBD product that fits your lifestyle and wellness goals.
Understanding CBD
What is CBD?
CBD is a naturally occurring compound found in the cannabis plant. It is one of over 100 cannabinoids, which are chemical compounds that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). Unlike its more famous cousin THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), CBD does not cause a “high” or intoxicating effect. This makes it an attractive option for people looking for relief from pain, anxiety, and other ailments without the mind-altering effects of cannabis or certain pharmaceutical drugs.
Where Does CBD Come From?
CBD is typically extracted from hemp, a variety of the cannabis plant that contains high levels of CBD and very low levels of THC (less than 0.3%). Hemp-derived CBD is legal in many parts of the world, including the United States, as long as it meets regulatory guidelines.
The Science Behind CBD
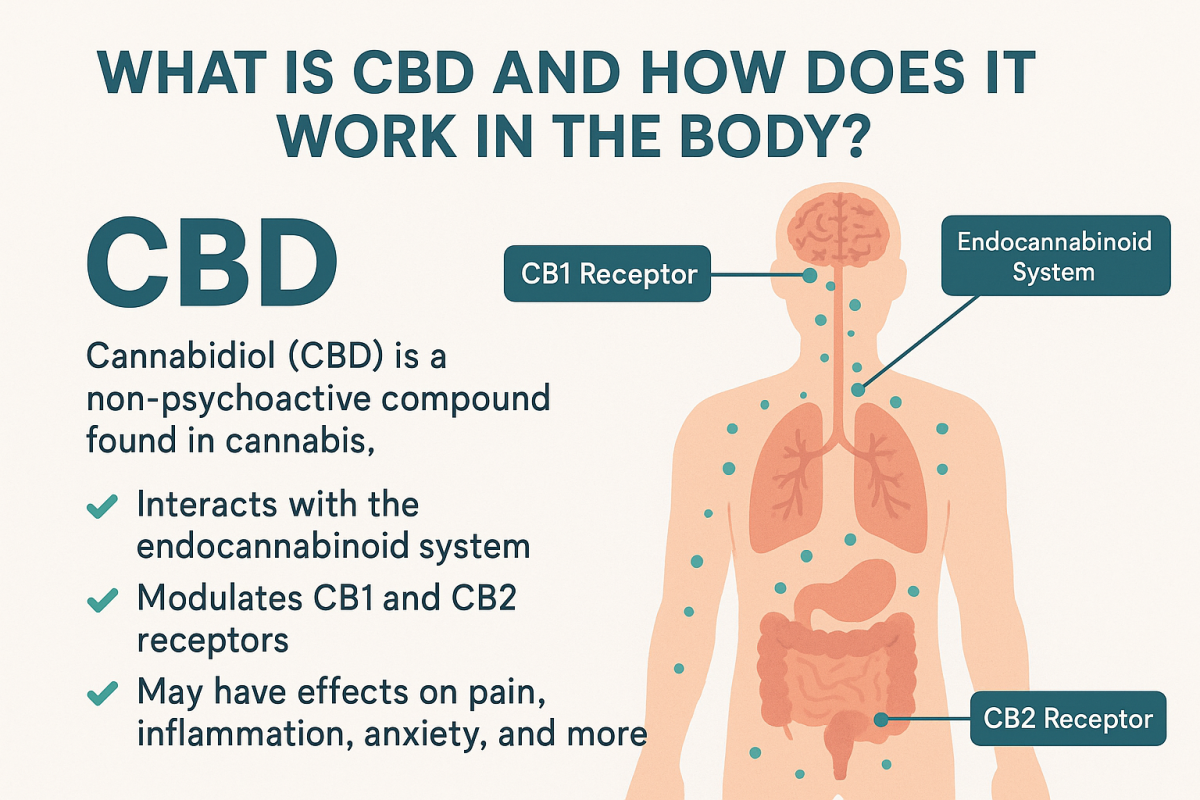
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
To understand how CBD works in the body, it’s essential to first understand the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a complex cell-signaling system found in all mammals that plays a critical role in regulating various physiological processes, including:
- Pain sensation
- Mood and stress
- Sleep
- Appetite
- Immune response
- Inflammation
The ECS consists of three main components:
- Endocannabinoids – Naturally produced cannabinoids within the body
- Receptors – Found throughout the body (mainly CB1 and CB2 receptors)
- Enzymes – Responsible for breaking down endocannabinoids
How CBD Interacts with the ECS
Unlike THC, which directly binds to CB1 receptors in the brain to produce psychoactive effects, CBD interacts with the ECS in a more indirect way. It is believed to influence the ECS by:
- Enhancing the body’s natural production of endocannabinoids
- Inhibiting the enzymes that break them down
- Modulating receptor activity, particularly the CB2 receptors, which are involved in inflammation and immune response
Additionally, CBD also interacts with other non-cannabinoid receptors in the body, such as:
- Serotonin receptors (5-HT1A): Involved in anxiety, mood, and pain regulation
- TRPV1 receptors: Related to pain and inflammation
Potential Health Benefits of CBD
While research on CBD is still ongoing, numerous studies and anecdotal evidence suggest that it may offer a variety of health benefits:
1. Pain Relief
CBD may help reduce chronic pain by influencing endocannabinoid receptor activity and reducing inflammation. It has shown promise in conditions like arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and fibromyalgia.
2. Anxiety and Stress Reduction
CBD is believed to have anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects. By interacting with serotonin receptors, it may help ease symptoms of anxiety, social phobia, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
3. Sleep Improvement
Many users report improved sleep quality and reduced insomnia after using CBD. This may be due to its calming effects and ability to address underlying causes like anxiety or pain.
4. Neuroprotective Properties
CBD has been studied for its potential to help protect the nervous system. Research has explored its role in treating neurological disorders like epilepsy (particularly Dravet syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome), Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Effects
CBD’s interaction with CB2 receptors may help reduce inflammation, making it a possible treatment for conditions such as acne, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even certain autoimmune disorders.
Is CBD Safe?
Side Effects and Considerations
CBD is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, even at high doses. However, some individuals may experience side effects such as:
- Fatigue
- Changes in appetite
- Diarrhea
- Dry mouth
It’s also important to note that CBD can interact with certain medications, particularly those that are metabolized by the liver enzyme CYP450. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting CBD, especially if you are taking prescription drugs.
Forms of CBD Products
CBD is available in a variety of forms, including:
- CBD Oil and Tinctures: Fast-acting and easy to dose under the tongue
- CBD Edibles: Such as gummies or chocolates for a tasty, longer-lasting effect
- CBD Capsules and Pills: Convenient and consistent dosing
- Topicals: Creams, balms, and lotions for localized pain or skin issues
- Vapes: Inhaled CBD for fast relief, though safety is debated
Conclusion
CBD is a fascinating compound with promising therapeutic potential. By interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system and other receptor pathways, it may help regulate pain, mood, sleep, and more. While research is still ongoing, the existing evidence and user experiences point toward a variety of possible benefits with minimal side effects.
As with any supplement or treatment, it’s best to approach CBD with informed caution. Start with a low dose, consult a medical professional if needed, and choose high-quality, lab-tested products for the best results.